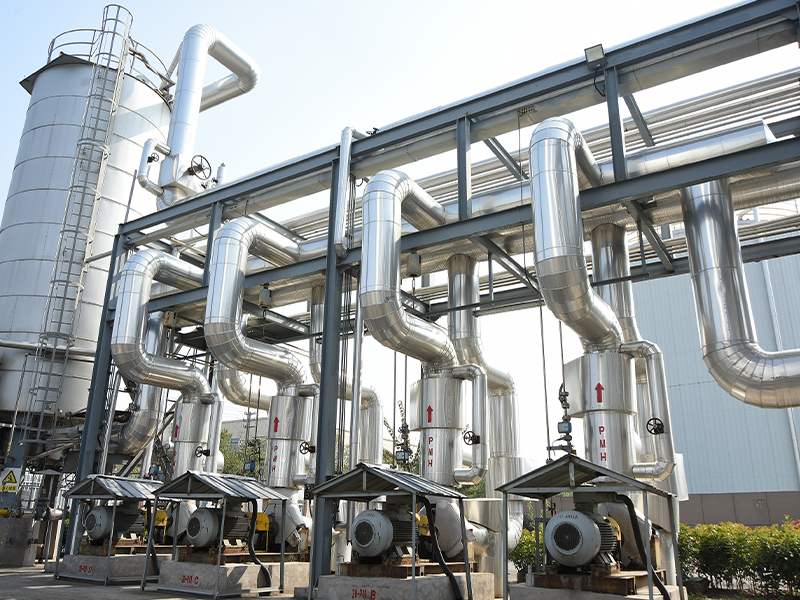
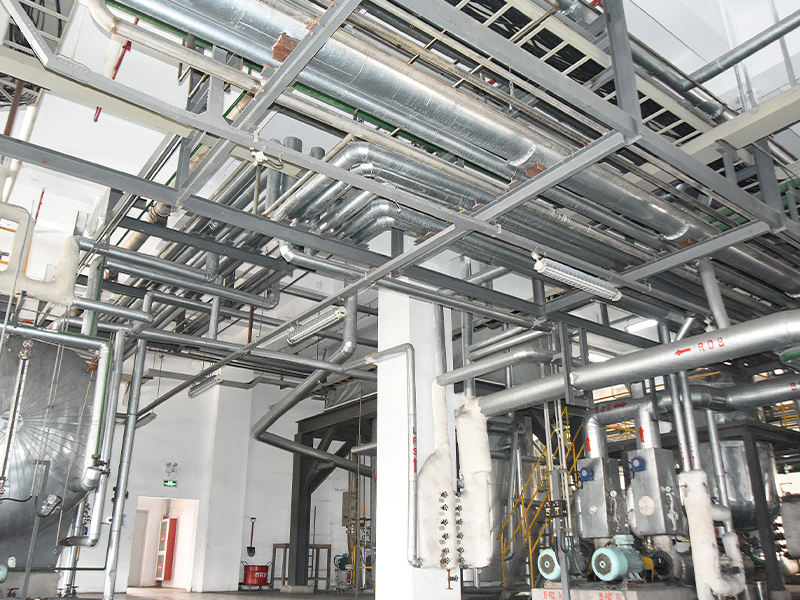
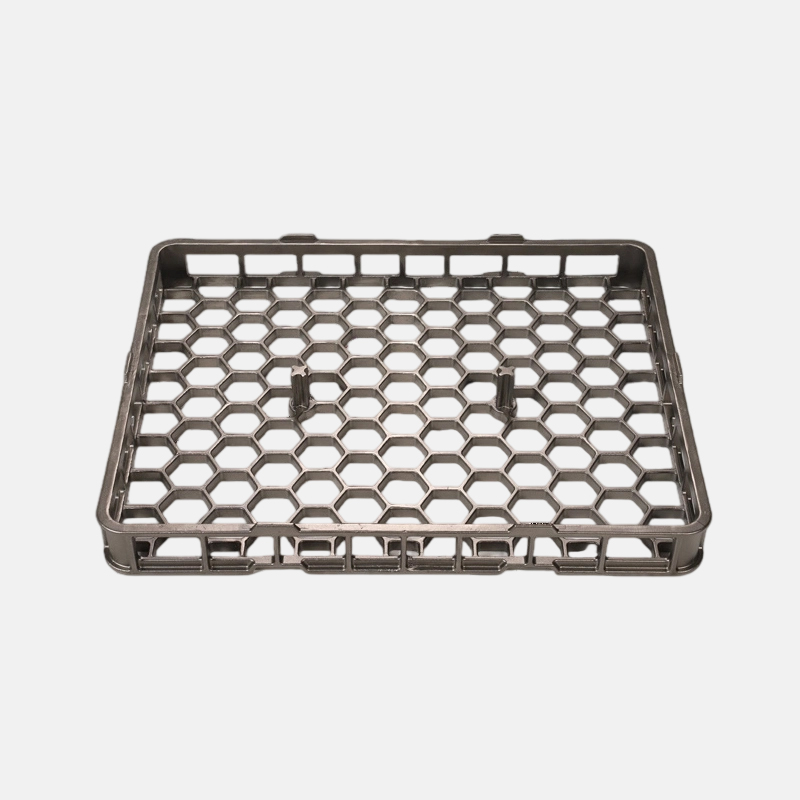
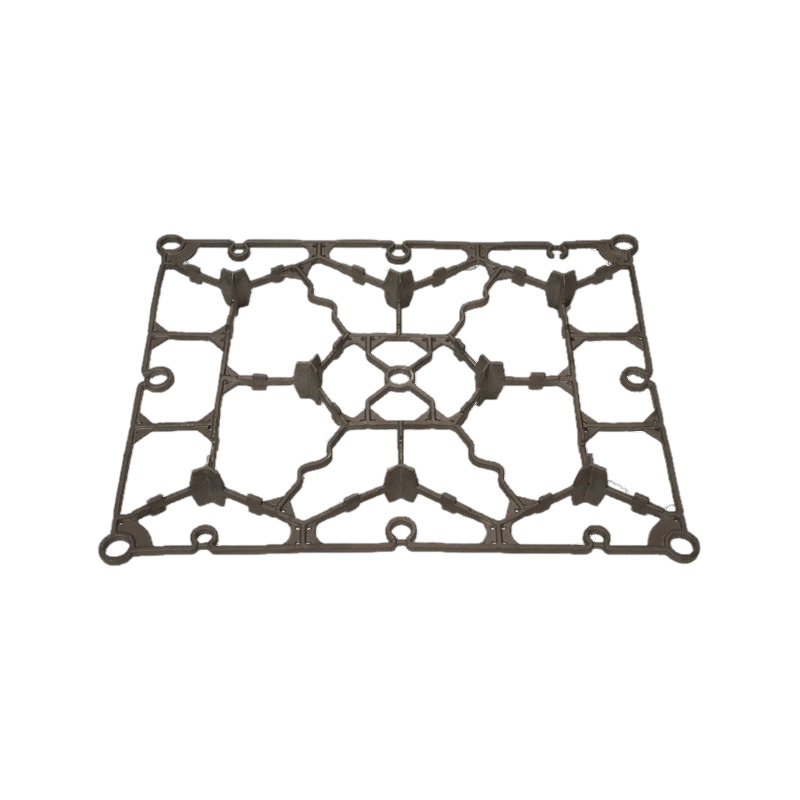
A Heat Treatment Tray is a critical accessory used in high-temperature industrial processes where metal components require controlled heating, soaking, and cooling to achieve specific mechanical properties. These trays are designed to withstand extreme thermal stress, repeated heating cycles, and corrosive furnace atmospheres while maintaining dimensional stability and load-bearing strength.
Across industries such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace, metallurgy, energy, and tooling, the Heat Treatment Tray plays an essential role in ensuring process efficiency, product consistency, and operational safety. As heat treatment technologies continue to advance, the demand for durable, high-performance trays has grown significantly.
- 1 Why Heat Treatment Trays Are Essential in Industrial Processes
- 2 Common Applications of a Heat Treatment Tray Across Industries
- 3 Comparison of Heat Treatment Tray Applications by Industry
- 4 Heat Treatment Tray Materials and Design Considerations
- 5 Heat Treatment Trays vs Other Furnace Support Solutions
- 6 Impact of Heat Treatment Trays on Production Efficiency
- 7 Future Trends in Heat Treatment Tray Applications
- 8 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 9 Conclusion
Why Heat Treatment Trays Are Essential in Industrial Processes
Industrial heat treatment processes—such as annealing, carburizing, nitriding, quenching, tempering, and sintering—require components to be placed securely inside furnaces. A Heat Treatment Tray provides a stable platform that supports parts, maintains spacing for uniform heat distribution, and protects both the components and furnace equipment.
- Structural support: Holds heavy or complex-shaped parts during high-temperature exposure
- Thermal stability: Resists deformation and cracking under repeated heating cycles
- Process consistency: Ensures even heat flow and predictable metallurgical results
- Operational efficiency: Enables batch processing and automation compatibility
Common Applications of a Heat Treatment Tray Across Industries
Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive industry is one of the largest users of Heat Treatment Trays. Components such as gears, shafts, bearings, fasteners, and suspension parts undergo heat treatment to improve hardness, fatigue resistance, and wear performance.
Heat Treatment Trays used in automotive applications are often designed to accommodate high-volume batch processing while maintaining precise part positioning. This helps ensure consistent hardness profiles and reduces distortion during quenching and cooling stages.
Aerospace and Aviation Industry
Aerospace components demand extremely tight tolerances and exceptional material integrity. Heat Treatment Trays are widely used for treating turbine blades, structural brackets, landing gear parts, and engine components made from nickel-based alloys, titanium alloys, and high-strength steels.
In this sector, trays must offer:
- Excellent creep resistance at elevated temperatures
- Minimal thermal expansion to protect dimensional accuracy
- Compatibility with vacuum and controlled-atmosphere furnaces
Metallurgy and Foundry Operations
In metallurgical plants and foundries, Heat Treatment Trays are used for stress relieving castings, normalizing forged components, and preheating materials before further processing. Their robust design allows them to carry heavy loads without warping or cracking.
Trays used in this environment are often manufactured from high-temperature alloys such as heat-resistant stainless steel or nickel-chromium-based materials to withstand oxidation and scale formation.
Tooling and Die Manufacturing
Tool steels used in molds, dies, punches, and cutting tools require precise heat treatment to achieve optimal hardness and toughness. Heat Treatment Trays ensure that these tools are evenly exposed to temperature changes, reducing the risk of uneven hardening or internal stress buildup.
Stackable tray designs are particularly popular in tooling heat treatment, as they maximize furnace space utilization while maintaining airflow between parts.
Powder Metallurgy and Sintering Processes
In powder metallurgy, green parts are placed on Heat Treatment Trays during sintering to achieve final density and mechanical strength. Trays used in these processes must provide excellent surface stability and resistance to chemical reactions with sintered materials.
Special tray designs may include perforations or mesh structures to improve gas circulation and temperature uniformity inside sintering furnaces.
Energy, Oil, and Gas Equipment Manufacturing
Components used in power generation, oil exploration, and gas transmission—such as valves, flanges, pressure vessels, and pipeline fittings—often require heat treatment to improve strength and corrosion resistance. Heat Treatment Trays support these large, heavy components throughout prolonged heating cycles.
Comparison of Heat Treatment Tray Applications by Industry
| Industry | Main Components Treated | Key Tray Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Gears, shafts, fasteners | High load capacity, batch efficiency |
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, brackets | Dimensional stability, alloy compatibility |
| Metallurgy | Castings, forgings | Oxidation resistance, durability |
| Tooling | Molds, dies, cutting tools | Uniform heat distribution |
| Energy & Oil | Valves, pressure components | Heavy-load support, long service life |
Heat Treatment Tray Materials and Design Considerations
The performance of a Heat Treatment Tray largely depends on its material composition and structural design. Common materials include:
- Heat-resistant stainless steel: Good oxidation resistance and cost efficiency
- Nickel-chromium alloys: Superior strength at high temperatures
- Cast heat-resistant alloys: Ideal for complex tray geometries
Design factors often include load distribution, tray thickness, rib reinforcement, and compatibility with automated handling systems.
Heat Treatment Trays vs Other Furnace Support Solutions
While alternatives such as baskets, racks, and fixtures are also used in furnaces, Heat Treatment Trays offer distinct advantages:
- Trays vs Baskets: Trays provide better support for flat or heavy components, while baskets are more suitable for small loose parts
- Trays vs Racks: Trays offer greater stability during quenching and transport
- Trays vs Fixtures: Trays are more versatile and cost-effective for batch processing
Impact of Heat Treatment Trays on Production Efficiency
The correct selection and application of a Heat Treatment Tray can significantly improve furnace productivity. Benefits include reduced downtime, longer service life, improved part quality, and lower maintenance costs.
Optimized tray design also supports lean manufacturing by reducing scrap rates and rework caused by uneven heating or part distortion.
Future Trends in Heat Treatment Tray Applications
As industries adopt higher-temperature processes and more advanced alloys, Heat Treatment Trays are evolving to meet new challenges. Emerging trends include lightweight alloy designs, improved resistance to carburizing and nitriding atmospheres, and modular tray systems compatible with Industry 4.0 automation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the primary function of a Heat Treatment Tray?
The main function of a Heat Treatment Tray is to support and position components during high-temperature processes, ensuring uniform heating and protecting both parts and furnace equipment.
How long does a Heat Treatment Tray typically last?
Service life depends on material quality, operating temperature, load conditions, and furnace atmosphere. High-quality trays can last several years under proper usage.
Can Heat Treatment Trays be customized?
Yes, many manufacturers offer custom-designed Heat Treatment Trays tailored to specific component shapes, furnace dimensions, and process requirements.
Are Heat Treatment Trays suitable for continuous furnaces?
Heat Treatment Trays are widely used in both batch and continuous furnaces, provided they are designed for conveyor compatibility and repeated thermal cycling.
How does tray design affect heat treatment quality?
Tray design influences airflow, heat distribution, and load stability. A well-designed Heat Treatment Tray helps prevent uneven heating, distortion, and surface defects.
Conclusion
From automotive and aerospace manufacturing to metallurgy and energy production, the Heat Treatment Tray remains a fundamental component of industrial heat treatment operations. Its versatility, durability, and impact on process quality make it indispensable across a wide range of applications. As industrial demands continue to grow, the role of advanced Heat Treatment Tray solutions will become even more critical in achieving efficiency, reliability, and consistent product performance.
 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى