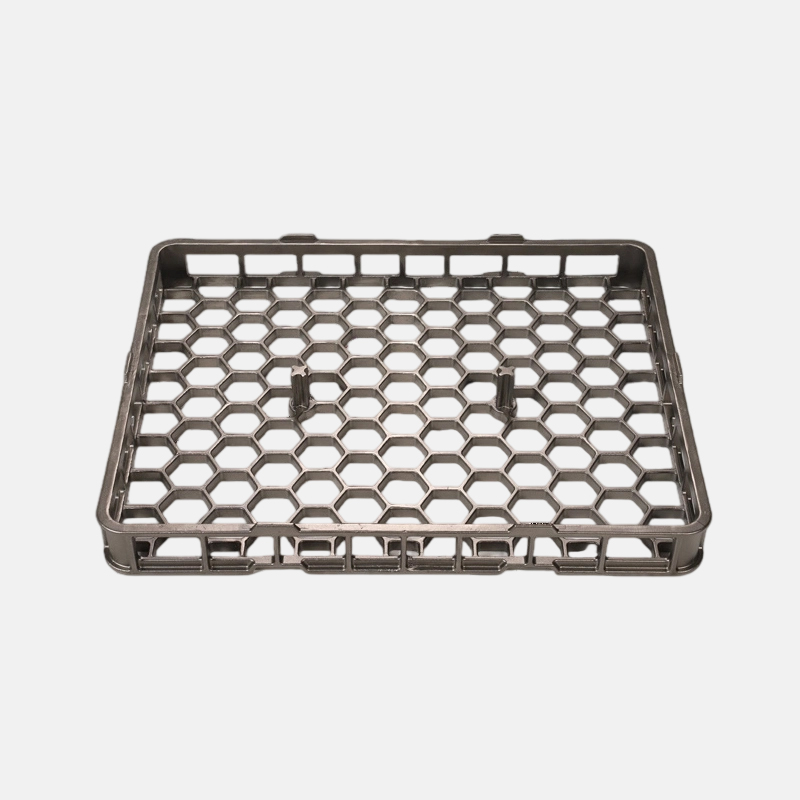
Heat Treatment Trays are essential components in industrial and manufacturing processes, designed to withstand high temperatures, mechanical stress, and chemical exposure. They play a vital role in heat treatment operations such as annealing, tempering, quenching, and sintering of metals and alloys. Choosing the right material for a Heat Treatment Tray directly impacts its durability, performance, and safety in demanding industrial environments.
- 1 Key Requirements for Heat Treatment Tray Materials
- 2 Common Materials Used for Heat Treatment Trays
- 3 Material Comparison for Heat Treatment Trays
- 4 Factors Influencing Material Selection
- 5 Best Practices for Extending Tray Lifespan
- 6 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 6.1 Q1: Can aluminum trays be used for high-temperature heat treatment?
- 6.2 Q2: Why is stainless steel preferred over carbon steel in some applications?
- 6.3 Q3: Are ceramic trays durable for industrial use?
- 6.4 Q4: How does nickel alloy compare to stainless steel for heat treatment trays?
- 6.5 Q5: What is the most cost-effective material for heat treatment trays?
- 7 Conclusion
Key Requirements for Heat Treatment Tray Materials
Durable Heat Treatment Trays must meet several crucial requirements to ensure optimal performance:
- High-temperature resistance: Trays must endure prolonged exposure to temperatures often exceeding 1000°C without warping or degrading.
- Mechanical strength: Trays should support heavy loads, including metal parts and industrial components, without bending or breaking.
- Corrosion resistance: Exposure to chemicals, oils, or salts during treatment demands materials that resist oxidation and corrosion.
- Dimensional stability: The tray must maintain shape and size during repeated heating and cooling cycles.
- Ease of cleaning: Smooth surfaces that do not trap residues ensure hygiene and longevity of the tray.
Common Materials Used for Heat Treatment Trays
Several materials are used in the construction of Heat Treatment Trays, each offering distinct advantages and limitations:
1. Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is one of the most popular materials for industrial heat treatment trays. Key benefits include:
- Excellent resistance to high temperatures and thermal cycling.
- Strong corrosion resistance due to chromium and nickel content.
- Durability and mechanical strength for heavy-duty applications.
Common grades include 304 and 316 stainless steel, which differ in corrosion resistance and cost. 316 stainless steel offers better resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for trays exposed to harsh environments.
2. Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is widely used for trays that require high mechanical strength but are not exposed to aggressive chemicals. Features include:
- Superior strength and load-bearing capacity.
- Good thermal conductivity, allowing even heating of parts.
- Lower cost compared to stainless steel.
However, carbon steel is prone to rust if exposed to moisture or corrosive environments. Coatings such as enamel or ceramic can enhance durability.
3. Aluminum
Aluminum trays are lighter than steel options and provide certain advantages:
- Excellent heat conduction for uniform temperature distribution.
- Lightweight design reduces handling effort.
- Moderate corrosion resistance, especially when anodized.
Aluminum trays are suitable for processes with moderate temperatures but may deform under extreme heat, making them less suitable for high-temperature industrial heat treatment compared to steel trays.
4. Ceramic and Refractory Materials
Ceramic and refractory trays are used in specialized applications where extreme heat resistance is required, such as sintering or annealing of superalloys. Key features include:
- Resistance to temperatures above 1200°C without deformation.
- High chemical inertness, preventing reactions with treated materials.
- Excellent dimensional stability under thermal cycling.
The main drawback is brittleness. Ceramic trays must be handled carefully to avoid cracking or chipping.
5. Nickel Alloys
High-performance nickel-based alloys are used in heat treatment trays designed for specialized industrial processes. Benefits include:
- Exceptional high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance.
- Resistance to thermal fatigue and oxidation.
- Long service life in demanding environments.
Nickel alloy trays are more expensive and generally reserved for critical applications where other materials may fail.
Material Comparison for Heat Treatment Trays
| Material | Temperature Resistance | Corrosion Resistance | Mechanical Strength | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Up to 1100°C | High | High | Medium-High |
| Carbon Steel | Up to 900°C | Low (requires coating) | Very High | Low-Medium |
| Aluminum | Up to 600°C | Moderate | Medium | Medium |
| Ceramic | Up to 1600°C | High | Low (brittle) | Medium-High |
| Nickel Alloys | Up to 1200°C+ | Very High | High | High |
Factors Influencing Material Selection
When selecting materials for a Heat Treatment Tray, consider:
- Operating temperature: Choose a material that withstands the maximum temperature of the process.
- Load capacity: Ensure the tray supports the weight of the workpieces.
- Chemical exposure: Consider resistance to oxidation, acids, or salts.
- Frequency of use: High-cycle applications may require stronger or coated materials.
- Budget and lifecycle cost: Sometimes a higher initial investment in durable materials saves maintenance and replacement costs.
Best Practices for Extending Tray Lifespan
To maximize the service life of a Heat Treatment Tray:
- Avoid thermal shock by gradually heating and cooling the tray.
- Regularly inspect for cracks, corrosion, or warping.
- Clean trays after each use to prevent chemical or residue buildup.
- Use coatings such as ceramic or enamel on steel trays for added corrosion protection.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can aluminum trays be used for high-temperature heat treatment?
Aluminum trays are suitable for moderate temperatures, typically up to 600°C. For higher-temperature processes, stainless steel or ceramic trays are recommended to avoid deformation and loss of mechanical strength.
Q2: Why is stainless steel preferred over carbon steel in some applications?
Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and long-term durability in environments with exposure to chemicals, moisture, or oxidation. Carbon steel may rust quickly unless properly coated.
Q3: Are ceramic trays durable for industrial use?
Ceramic trays can withstand very high temperatures and are chemically inert. However, they are brittle and can crack if mishandled or exposed to mechanical shocks.
Q4: How does nickel alloy compare to stainless steel for heat treatment trays?
Nickel alloys excel in extreme high-temperature applications with excellent thermal fatigue resistance and corrosion protection. Stainless steel is strong and cost-effective but may not perform as well in ultra-high-temperature environments.
Q5: What is the most cost-effective material for heat treatment trays?
Carbon steel is generally the most cost-effective for standard industrial applications where corrosion is controlled. For long-term durability and resistance to chemicals, stainless steel provides a better lifecycle value despite higher initial costs.
Conclusion
The choice of material for a Heat Treatment Tray is critical to ensure efficiency, safety, and longevity in industrial operations. While stainless steel remains the most versatile option, carbon steel, aluminum, ceramic, and nickel alloys each have specialized roles depending on temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical demands. Careful consideration of operating conditions, material properties, and maintenance practices ensures optimal performance and extended service life for every heat treatment application.
 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى