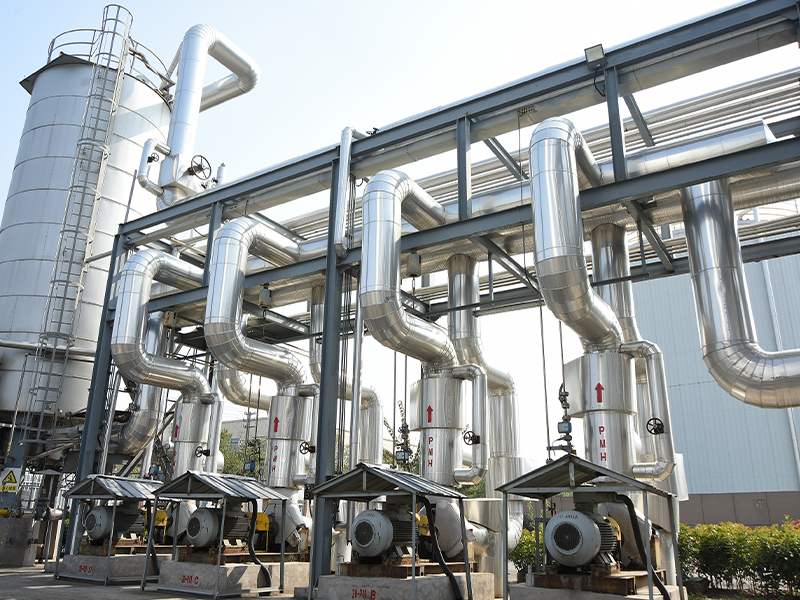
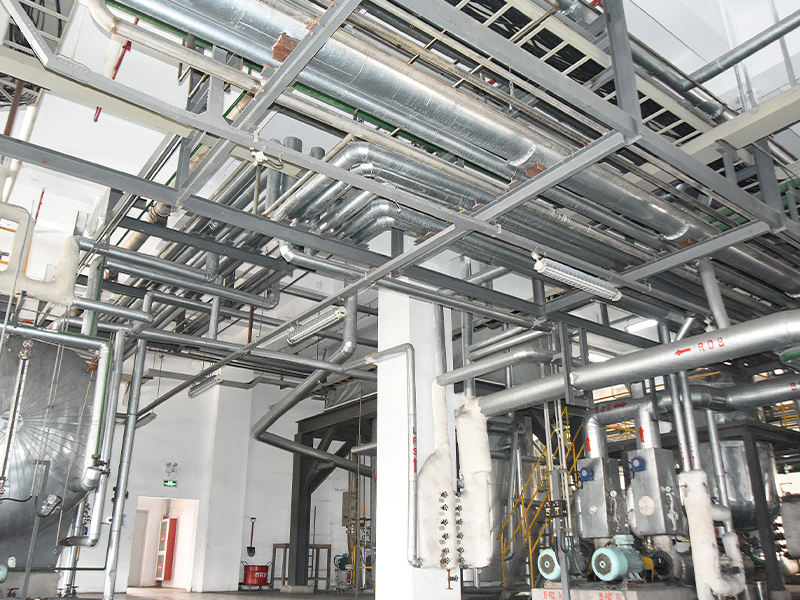
Centrifugal casting is a specialized metal casting process that utilizes centrifugal force to produce high-integrity components with uniform microstructures. This method is widely employed in industries such as manufacturing, aerospace, and energy due to its ability to create parts with minimal defects and enhanced mechanical properties. By rotating a mold at high speeds, centrifugal casting ensures the even distribution of molten metal, resulting in dense and reliable products.
The Process of Centrifugal Casting
The centrifugal casting process involves several sequential steps to achieve precise component formation. It begins with the preparation of a mold, typically made from steel or graphite, which is rotated around its axis. The steps are as follows:
-
Melting the metal: Raw materials are heated in a furnace until they reach a molten state.
-
Pouring the metal: The molten metal is introduced into the rotating mold while it spins at controlled speeds.
-
Centrifugal force distribution: As the mold rotates, centrifugal force pushes the metal outward against the mold walls, ensuring uniform thickness and eliminating impurities.
-
Cooling and solidification: The metal cools and solidifies under rotation, forming a hollow or solid shape depending on the mold design.
-
Extraction: Once solidified, the casting is removed from the mold for finishing processes like machining or heat treatment.
Types of Centrifugal Casting
Centrifugal casting can be categorized into distinct methods based on mold orientation and application requirements. Each type serves specific industrial needs:
-
True centrifugal casting: This method involves rotating a mold horizontally or vertically to produce symmetrical parts such as pipes and tubes without using a central core. It relies solely on centrifugal force to shape the metal.
-
Semi-centrifugal casting: Used for creating parts with rotational symmetry, such as wheels or gears, this approach employs a central core to form internal features while centrifugal force fills the mold cavity.
-
Centrifuge casting: In this technique, multiple molds are arranged around a central sprue and rotated to produce small, intricate components like jewelry or dental implants, leveraging centrifugal force for detailed replication.
Applications of Centrifugal Casting
Centrifugal casting is utilized in various sectors for manufacturing components that demand high strength and reliability. Common applications include:
-
Production of pipes and tubes for water supply, oil, and gas industries, where seamless construction reduces leakage risks.
-
Manufacturing of bearing sleeves and bushings in automotive and machinery, benefiting from the process's ability to yield wear-resistant surfaces.
-
Creation of cylinder liners and rings for engines, which require consistent material properties to withstand thermal and mechanical stress.
-
Fabrication of components for aerospace and defense, such as turbine parts, due to the method's capacity for producing defect-free structures.
Advantages and Limitations of Centrifugal Casting
Centrifugal casting offers several benefits but also presents certain constraints, as outlined below:
Advantages:
-
Enhanced density and mechanical properties: The centrifugal force reduces porosity and gas entrapment, leading to stronger, more durable castings.
-
Uniform microstructure: Rotation promotes even grain alignment, improving resistance to corrosion and fatigue.
-
Material efficiency: Minimal waste is generated, as excess metal can be reclaimed, and the process often requires less machining.
Limitations:
-
High initial setup costs: Specialized equipment and molds can be expensive, making it less suitable for small-scale production.
-
Geometric constraints: The process is ideal for cylindrical or symmetrical shapes but may not accommodate complex, asymmetrical designs.
-
Operational complexity: Precise control of rotation speed and temperature is necessary to avoid defects like segregation or uneven walls.
Centrifugal casting is a robust manufacturing technique that leverages centrifugal force to produce high-quality metal components. Its applications span critical industries, and while it has limitations in cost and geometry, its advantages in material integrity make it a valuable process. As technology advances, centrifugal casting continues to evolve, offering solutions for demanding engineering challenges.
 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى